
The Survey says that with the establishment of a Central Ministry, efforts to improve and streamline the skilling ecosystem were ramped up as the government launched the National Skill Development Mission as well as the National Policy on Skill Development and Entrepreneurship. Under the NEP 2020 also, there is a special focus on vocational education and skill development. Integration of vocational education with general education and mainstreaming of vocational education have been identified as the key reform in the education System of the country. The Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt Nirmala Sitharaman tabled Economic Survey 2022-23 in Parliament today.
Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) FY21 shows that formal vocational/technical training among youth (age 15- 29 years) and the working population (age 15-59 years) have improved in FY21 over FY19 and FY20. The improvement in skills has been for males and females, both in rural and urban sectors.
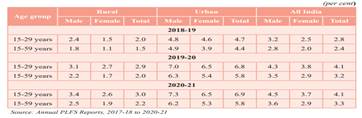
Distribution of persons who received formal vocational/technical training
As per the reports of the fourth round of the Quarterly Employment Survey (QES) (for Q4 FY22) in respect of establishments employing at least 10 workers in major nine sectors, 15.6 per cent of estimated establishments imparted formal skill training and 20.5 per cent imparted on-the-job training. The health sector had the highest percentage of estimated establishments imparting formal skill training (24.7 per cent) and on-the-job training (31.6 per cent), followed by financial services (20.4 per cent of establishments imparting formal training and 26.4 per cent imparting on-the-job training).
Skill Indian Mission
The Skill Indian Mission focuses on skilling, re-skilling and up-skilling through short term and long term training programmes. Under the Mission, the government, through more than 20 Central Ministries/Departments, is implementing various skill development schemes across the country. The advocacy of the programmes is being done through print media, electronic media, and State Governments’ campaigns. More and more areas are being aligned with the common framework spanning the skills ecosystem so that the outcomes of the Government skilling programmes are uniform across the skilling ecosystem.

The progress in some of these schemes is presented in Box:
|
Progress of Skill India Mission |
|
|
Skill Development Scheme |
Progress |
|
PMKVY was first launched in 2015. Presently, the third phase of PMKVY, i.e., PMKVY 3.0 is being implemented across the country since January 2021
PMKVY has two training components, viz., Short Term Training (STT) and Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL).
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Kendra set up at District level, are envisaged as state of the art, visible and aspirational model training Centres |
|
|
Jan Shikshan Sansthan Scheme provides for a lump sum annual grant is released to Jan Shikshan Sansthans (NGOs) for skill training to non-literate, neo-literates, persons with a rudimentary level of education and school dropouts up to class XII in the age group of 15-45 years. The priority groups are women, SC, ST, and other backward sections of society. |
|
|
National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme provides financial support to industrial establishments undertaking apprenticeship programmes under the Apprentices Act, 1961. |
|
|
Craftsmen Training Scheme provides long-term training in 149 trades through 14,938 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) across the country |
|
|
Craft Instructor Training Scheme provides comprehensive training both in skills and training methodology is imparted to the instructor trainees to make them conversant with the methodology of teaching and techniques of transferring hands-on skills, to train skilled manpower for the industry. |
|
|
Making India Skill Capital of the World |
With an aim to make India a Skill Capital of the World and improve mobility of Skilled manpower the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) International has been set up, which aims to create a network of institutions across India. This network of institutions will be called as Skill India International (SII) Network. It shall be created through the empanelment of state-of-the-art government and private institutions.
|
|
Skill Acquisition and Knowledge Awareness for Livelihood Promotion (SANKALP) is a World Bank loan-assisted programme launched in 2018 to decentralise skilling initiatives and align skill development programmes with local demand and aspirations of the youth |
|
*****
RM/SC/NB/AK/UD

